You can either watch the video tutorial for a quick walkthrough or follow the step-by-step written instructions below for more detailed guidance.
Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Large language models (LLMs) can do a lot and enable many applications, but there are scenarios where LLMs fall short. This often happens when you need to leverage private knowledge, update information periodically, or work with very large knowledge bases. This is why we use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) — a powerful approach for integrating dynamic and private information with generative AI.
Why Do We Need Retrieval-Augmented Generation?
To understand the necessity of RAG, consider this: if you ask an LLM about your company's revenue in the EMEA region for the previous year, it will likely respond that it doesn't have access to your financial data. Alternatively, it might generate an inaccurate response by guessing. This limitation exists because LLMs rely on pre-trained data, and there is no direct way for them to access proprietary, private, or frequently changing information.
LLMs like GPT-4 are trained on a vast dataset of publicly available content, including forums, blogs, and books. They are statistical models that predict text based on patterns and probabilities derived from this training data, rather than accessing specific sources of information. This means that the knowledge they provide is representative of general public knowledge — often accurate, but not always verifiable or complete.
Challenges of LLM-Only Solutions
When using only LLMs without supporting structures, several challenges arise:
- Static Knowledge: LLMs are frozen in time. The knowledge they hold is limited to what was available during the training period. Updating an LLM requires costly retraining or fine-tuning, and outdated information can be difficult to remove.
- Lack of Domain-Specific Knowledge: General-purpose LLMs are not trained on your company's proprietary data, such as revenue statements or project reports. This limits their ability to provide context-specific answers.
- Opaque Decision-Making: LLMs function as black boxes, making it impossible to trace back the exact sources behind a generated answer. This is problematic for enterprises that require verifiability and accountability.
- Costly and Complex to Train: Building and fine-tuning LLMs is expensive and requires significant technical expertise. Fine-tuning adds more knowledge to the model but doesn't solve the inherent issues of opacity and outdated information.
- Context Size Limitations: LLMs have limits on the amount of context they can handle in a single prompt. For example, GPT-4o can take up to 128,000 tokens — enough for a 100-page book, but insufficient for larger knowledge bases.
These challenges make LLMs unsuitable for scenarios where up-to-date, verifiable, and extensive information is required, especially for enterprise applications.
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation?
RAG augments the capabilities of LLMs by incorporating data retrieval mechanisms. It works in two phases:
- Building a Knowledge Base: The first phase involves building a vector database with your organization's knowledge. This includes raw documents, chunks of information, and their corresponding vector representations.
- Querying the Knowledge Base: In the second phase, when a user queries the system, a semantic search is performed on the vector database. The search results are then used to generate an enriched and context-specific response using an LLM.
Building a RAG Pipeline
The first step in creating a RAG pipeline is chunking — dividing large documents into smaller, meaningful sections called chunks. These chunks are then translated into vectors using an embedding model, which provides a numeric representation of the semantics of each chunk.
The vectors are stored in a vector database, which allows for efficient semantic searches. When a query is made, the system searches through these vectors to find the chunks that are semantically closest to the query. This enables us to provide highly relevant information without relying solely on the LLM's pre-trained knowledge.
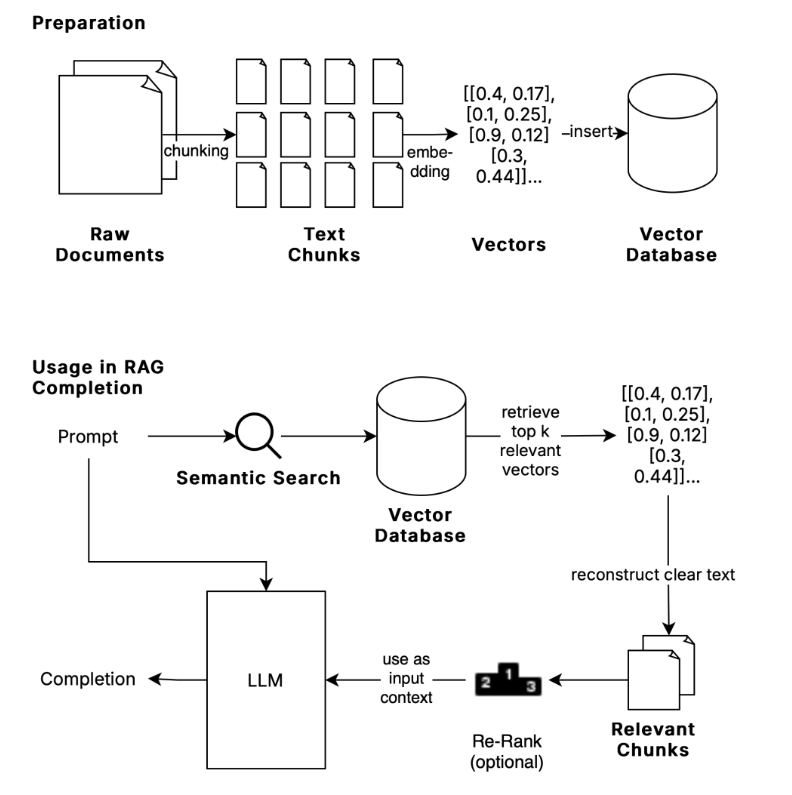
Embedding and Vector Representation
An embedding model translates each chunk into a vector, capturing the semantic meaning of the text. These vectors are then stored in a vector database. For example, similar sentences like "a little boy is walking" and "a little boy is running" will have similar vector representations, allowing the system to recognize their semantic closeness.
Querying and Generating Responses
When a user makes a query, an embedding of that query is generated and compared to the stored vectors. The closest matching chunks are retrieved, and these chunks are then used to generate a response.
To further enhance quality, an optional step called retrieval reranking can be added. In this step, the top K results are fed into an LLM for re-ranking, ensuring the final output is both relevant and accurate.
Advantages of RAG Over LLM-Only Approaches
- Dynamic Knowledge: Unlike LLMs, RAG pipelines are not static. You can easily add, update, or delete information in the vector database, ensuring your knowledge base remains up to date.
- Domain-Specific Knowledge: With RAG, you can insert proprietary and domain-specific knowledge, giving your organization control over the data used in generating responses.
- Traceability: RAG enables traceability by allowing you to link the generated output back to its original source. This is particularly useful for enterprises that require verifiable information.
- Cost Efficiency: Embedding models and vector searches are much less costly compared to running large LLMs for every query. This makes RAG a cost-effective solution for handling large amounts of data.
- Handling Large Knowledge Bases: RAG allows you to efficiently work with large knowledge bases, avoiding the context size limitations inherent to LLMs.
Summary
Retrieval-Augmented Generation combines the strengths of LLMs with the flexibility and efficiency of data retrieval. By using RAG, you can overcome the limitations of LLM-only approaches, such as static knowledge, lack of domain-specific information, and high costs. RAG pipelines allow you to leverage private knowledge, ensure verifiability, and create dynamic, enterprise-grade AI solutions.
For enterprises looking to harness the power of generative AI in a secure, scalable, and cost-efficient way, RAG provides a compelling solution.
Next Steps
To get started with building your own RAG pipeline, explore our detailed guides on setting up vector databases, choosing the right embedding models, and integrating retrieval mechanisms into your existing workflows. RAG can transform how your organization leverages AI, enabling more accurate, efficient, and traceable insights.