Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that combines language models with external data sources to provide more accurate, up-to-date, and verifiable answers. Instead of relying solely on the model’s internal knowledge, RAG retrieves relevant documents or facts from a knowledge base and incorporates them into the prompt, enabling the model to generate responses grounded in real-world information.
RAG is especially valuable for knowledge-intensive tasks, fact-based question answering, and scenarios where the information required may not be present in the model’s training data.
Use When
- The task requires information not in the model’s training data.
- You need factual, current, or domain-specific knowledge.
- Traceability and source attribution are important.
Pattern
- Retrieve relevant documents or facts from an external source (e.g., database, search engine, vector store).
- Provide the retrieved information to the model as context for answering the question.
- Optionally, prompt the model to cite or reference the sources used.
Examples
Example 1: Factual Question Answering
Given the following article, answer: What are the main causes of climate change?
[Paste article here]
Model output:
The main causes of climate change are greenhouse gas emissions from burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
Example 2: Company Knowledge Base (new)
Using the provided company knowledge base, summarize the latest product updates.
[Insert knowledge base excerpt]
Model output:
Recent product updates include the launch of a new analytics dashboard, improved API integration, and enhanced security features.
Example 3: RAG with Source Attribution
Retrieve relevant documents about the 2024 Paris Olympics and answer: What are the new sports introduced?
[Retrieved context: ...]
Model output:
The 2024 Paris Olympics will introduce breaking (breakdancing) as a new sport. [Source: olympics.com]
✅ Benefits
- Accuracy: Reduces hallucinations by grounding answers in real data
- Freshness: Enables access to up-to-date or proprietary information
- Traceability: Allows linking answers to their original sources
⚠️ Pitfalls
- Quality depends on the relevance and accuracy of retrieved data
- May require integration with search, database, or vector store tools
- Retrieval step can introduce latency or complexity
The quality of RAG outputs is only as good as the quality of your knowledge base and retrieval system!
RAG System Architecture
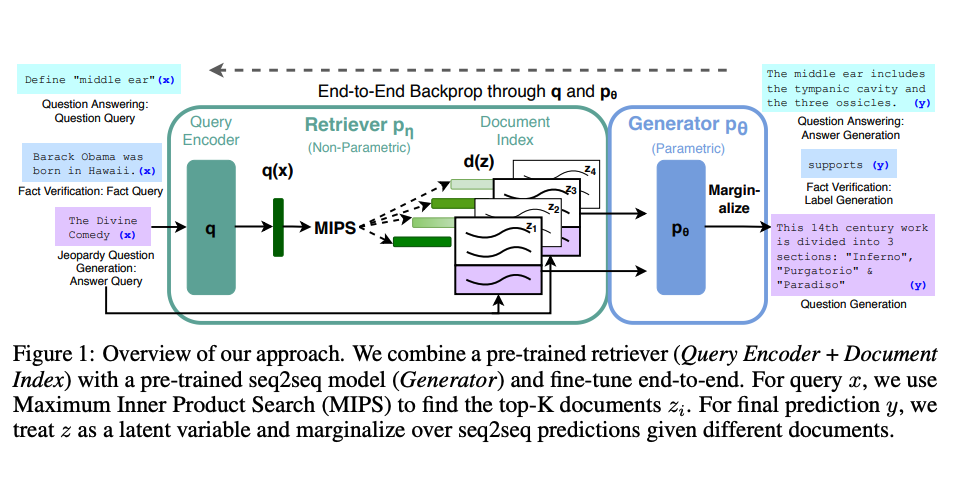
The diagram above shows the Retrieval-Augmented Generation framework that combines an information retrieval component with a text generator model. The following illustrates the RAG process flow:
User Query: "What is quantum computing?"
│
▼
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ QUERY │────▶│ RETRIEVAL │
│ PROCESSING │ │ ENGINE │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐
│ KNOWLEDGE BASE │
│ • Research docs │
│ • Wiki articles │
│ • Tech papers │
└─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐
│ RELEVANT DOCS │
│ [Doc1, Doc2...] │
└─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ PROMPT │◀────│ CONTEXT │
│ GENERATION │ │ ASSEMBLY │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ LANGUAGE │────▶│ GENERATED │
│ MODEL │ │ RESPONSE │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
This architecture ensures responses are grounded in factual, retrieved information rather than relying solely on the model's parametric knowledge.
References
- Lewis, P., Perez, E., Piktus, A., Petroni, F., Karpukhin, V., Goyal, N., ... & Riedel, S. (2020). Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. NeurIPS 2020.